- vortextimes.com
- March 10, 2024
- 11:46 pm
- No Comments
Estrogen’s Protective Role Unveiled in Combatting Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Cancer :
Recent studies from Sweden’s prestigious Karolinska Institutet has provided critical new insight into the protecting role of oestrogen in opposition to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), a condition that is becoming more usual together with the global weight problems pandemic. Published in Molecular Systems Biology, the take a look at sheds mild on the protective mechanism of oestrogen and provides novel insights which have the potential to convert the remedy paradigm for liver cancer and fatty liver disease.
Table of Contents
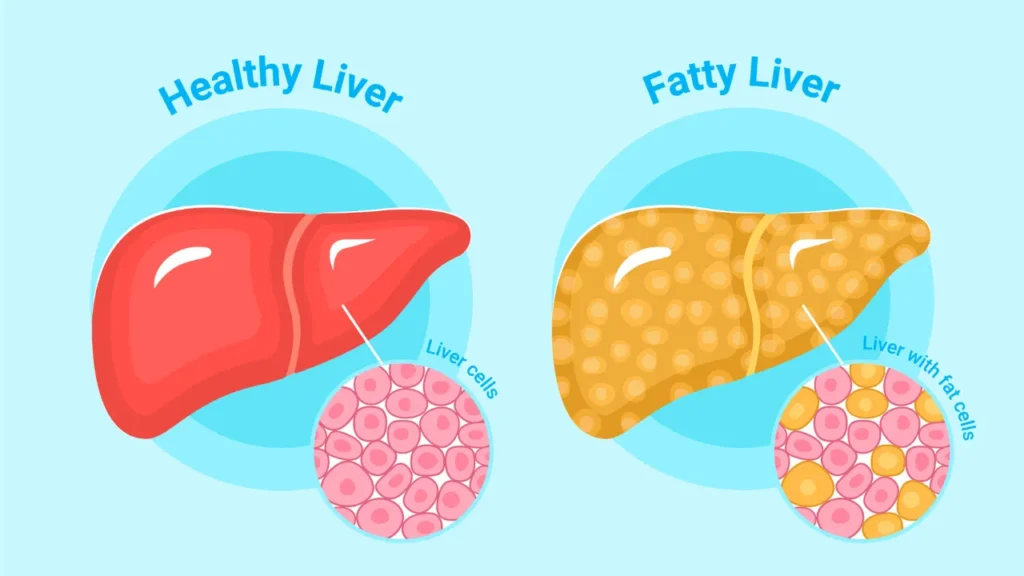
Understanding the Surge of Fatty Liver Disease:
Gender Disparity and Estrogen's Protective Effect:
Crucial Insights Unveiled:

Translating Findings into Potential Therapies:
A Promising Future:
Conclusion:
FAQs
1. What is the significance of the recent research from Karolinska Institutet regarding estrogen and fatty liver disease?
• The study clarifies the protective role of oestrogen against Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), providing information about possible therapies for both the illness and the liver cancer it is linked to.
2. What is MASLD, and how does it differ from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)?
• MASLD, formerly known as NAFLD, is the term used to describe fatty liver disease that is not brought on by excessive alcohol consumption but rather by metabolic dysfunction. It includes a wider range of liver pathologies linked to metabolic syndrome and obesity.
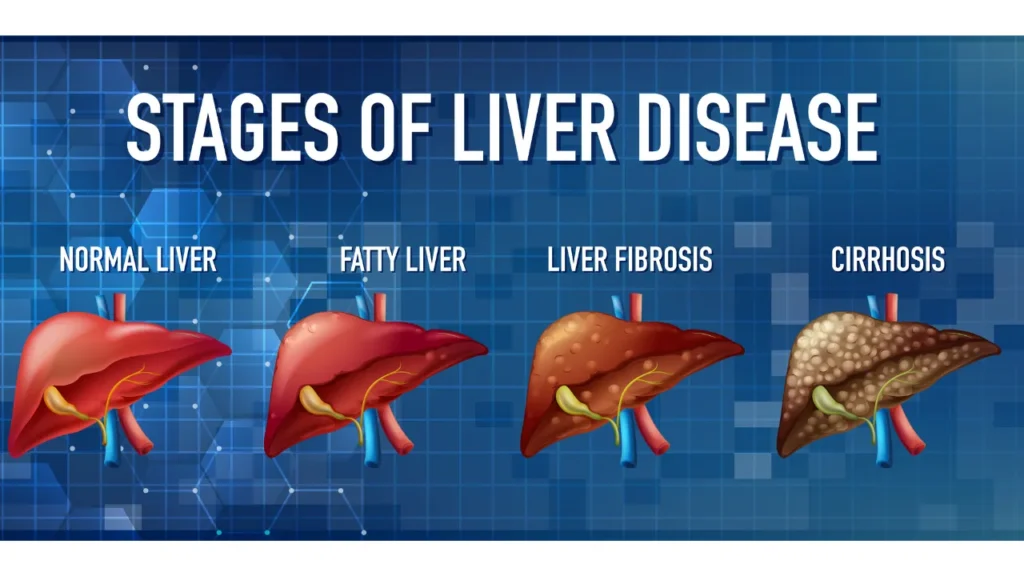
3. What is the prevalence of MASLD globally, and how severe can it become?
• Up to one in three adults globally suffer from MASLD; severe cases carry a significant risk of developing liver cancer and cirrhosis.
4. Why is there a gender discrepancy in the prevalence of MASLD, with men being disproportionately affected?
• The presence of oestrogen naturally shields premenopausal women from MASLD. This hormone is essential for protecting liver cells from accumulating fat.
5. What is the mechanism by which estrogen protects against MASLD?
• TEAD1, a protein that controls how much fat is absorbed by liver cells, is less active when oestrogen is present. Decreased TEAD1 activity prevents fat from accumulating in the liver, which slows the progression of MASLD.
6. How was the protective role of estrogen elucidated in the study?
Using mice given a high-fat diet, researchers performed genetic analyses to see how oestrogen supplementation affected TEAD1 activity and liver fat accumulation. These results were confirmed by additional studies conducted on human liver cells.
7. What is TEAD1, and why is it significant in the context of fatty liver disease?
• A protein called TEAD1 is essential for controlling how much fat is absorbed by liver cells. The aetiology of MASLD is thought to be related to TEAD1 activity dysregulation.
8. How does blocking TEAD1 offer potential therapeutic benefits for MASLD and liver cancer?
• By blocking TEAD1 activity, liver cells are protected from the accumulation of harmful fat, which may stop MASLD from progressing to more serious liver pathologies like liver cancer.
9. What are the implications of these findings for future treatment strategies?
• The identification of TEAD1 as a therapeutic target provides opportunities for the creation of innovative medications intended to treat and prevent MASLD. TEAD1-targeting drugs are being tested in clinical trials to see how well they work against fatty liver disease.
10. What are the next steps in research and clinical practice following these groundbreaking discoveries?
• Ongoing studies will concentrate on deciphering the protective mechanisms of oestrogen and investigating new therapeutic targets for MASLD. In order to maximise patient care, specific strategies based on gender and hormonal status will be prioritised in clinical practice.